We open a new page of Apollo’s seafood guide with a gastronomic delight: cod. The ham of the sea or the calf of the ocean, as it is called because of its culinary potential similar to these delicacies, is among the most consumed fish in Europe. This delicacy has gone from being a modest fish typical of Lent to becoming popular in avant-garde cuisine, as we explained in a previous post.
From cod, as from pork, practically all the meat is used. Among the most consumed parts are the belly, tails and loin. Its guts are also highly valued, with a texture similar to tripe when cooked. In fact, the guts are the cod’s swim bladder, a hydrostatic organ that allows them to star in scenes similar to those that appeared in The Matrix, when the characters were suspended in the air. In this case, of course, they do it in the aquatic environment. Thus, this kind of sack, similar to a balloon, is filled with air and allows them to modify their specific weight, either to remain still in the water or to ascend or descend at will.
Apart from tripe, a typical dish in Mediterranean areas such as Catalonia, tongue and kokotxas also serve as the basis for numerous recipes. We must not forget cod roe and cod liver, from which the popular cod oil is extracted, rich in Omega 3 fatty acids, beneficial for the heart and cardiovascular system, and in vitamins A and D, the latter of which is scarce in many diets despite being essential for the absorption of calcium or in the prevention of diseases such as rickets and osteoporosis.
Where is cod caught?
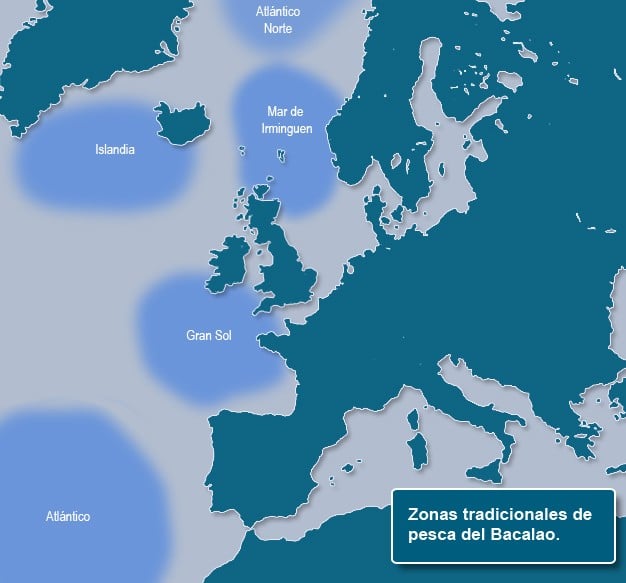
Cod inhabit cold waters of the North Atlantic. The largest fishing grounds for this species are located in the Barents Sea, very close to the Arctic. This fish is also found in the Baltic and the North Sea, although the warming of these waters due to climate change is displacing it to colder waters, according to recent studies. It is normally found at depths ranging from 150 to 200 meters, although it can also be found at depths of more than 600 meters.
What are the best known cod species?
- Gadus macrocephalus. Also called Pacific cod.
- Gadus morhua morhua. This species of European origin inhabits from the Bay of Biscay to the Barents Sea.
- Gadus morhua callaris. This species, also European, is found in the Baltic Sea.
- Gadus ogac. Name given to the Greenland cod.
What are the nutritional properties of cod?
Like other white fish, cod is low in fat, which makes it an exceptional ally if you are on a diet and want to keep in shape. It is also rich in protein, B vitamins, vital for the use of energy nutrients, potassium, which benefits the nervous system, and phosphorus, essential to strengthen bones and teeth. If the cod is salted, it is contraindicated for people with hypertension, cardiovascular problems or tendency to retain liquids due to its sodium content. However, if it has been properly desalted or is natural – either fresh or frozen – it is good for high blood pressure due to the proportion of potassium it contains.
Buy frozen cod
Apolo sells different varieties of frozen cod in various formats (belly, fillets, tails, etc), although this fish can also be purchased fresh, salted or canned. For its production, the company from Granada, based in Loja, uses state-of-the-art techniques in the freezing industry to preserve its original quality, as well as strict controls to maintain the cold chain. These are the varieties sold wholesale by the company, Andalusian leader in the frozen sector:
- Cod fillet in its salt point.
- Cod fillet Banord
- Cod centers
- Cod fillet Jumbo
- Extra cod fillet
- Extra Icelandic cod fillets
- Cod belly
- Cod in portion/ menu
Five interesting facts about cod
1. It is a typical Jamaican dish
2. Antarctic cod hibernates to save energy
3. Can survive up to 20 years
4. Some specimens can reach 100 kilos
5. It lays 7 million eggs, although few survive because other fish tend to feed on them.





